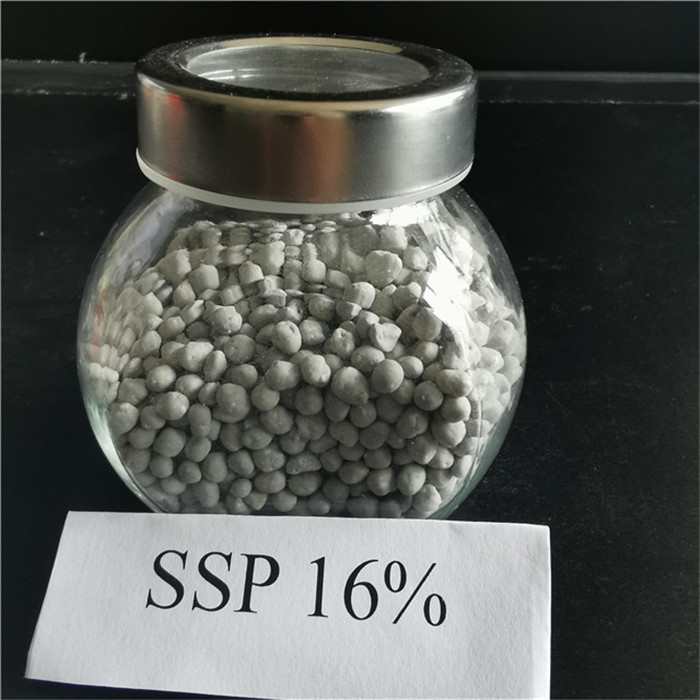
Description
| Chemical Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | Ca(H2PO4)2.H2O |
| CAS Number | 10031-30-8 |
| Phosphorus content | 7 to 9% (16 to 20% P2O5) |
| Calcium (Ca) content | 18 to 21% |
| S content | 11 to 12% |
| pH | < 2 |
| Use | Agricultural fertilizers, Crops |
| Application | |
| Period | Autumn, Spring |
| Method | #1.Main The main way to fertilize. Uniform distribution of fertilizer elements on the soil surface, maintaining roughly the same distance between solid fertilizer granules or liquid fertilizer drops. #2.During sowing Fertilizing simultaneously with crop seeding. The main purpose is to provide effective plant nutrition at the initial stages of development and growth. |
| Crops | All crops |
Agricultural Use
SSP is an excellent source of three plant nutrients. The P component reacts in soil similarly to other soluble fertilizers. The presence of both P and sulfur (S) in SSP can be an agronomic advantage where both of these nutrients are deficient. In agronomic studies where SSP is demonstrated to be superior to other P fertilizers, it is usually due to the S and/or Ca that it contains. When locally available, SSP has found widespread use for fertilizing pastures where both P and S are needed. As a source of P alone, SSP often costs more than other more concentrated fertilizers, therefore it has declined in popularity.
Management Practices
No special agronomic or handling precautions are required for SSP. Its agronomic effectiveness is similar to other dry or liquid phosphate fertilizers. The loss of P in surface runoff from fertilized fields can contribute to water quality problems. Farm practices that minimize this loss should be implemented.